Where Did Gothic Architecture Begin and What Era Was It From?
Table of Contents

Have you ever looked at a towering cathedral or a grand, pointed archway and felt completely drawn to its timeless beauty? Gothic architecture isn’t just about stone and structure, it’s a story of history, elegance, and artistry that still inspires homes and design today. Whether you’re curious about its origins or simply love incorporating classic styles into your space, this guide will take you on a journey through the fascinating Gothic era architecture.
Understanding Gothic Architecture — A Quick Overview
Before we explore where it all began, let’s make sure you’re familiar with the essentials of Gothic style architecture. This isn’t just a medieval curiosity, it’s a design movement that shaped much of Europe and continues to influence modern aesthetics.
What is Gothic Architecture?
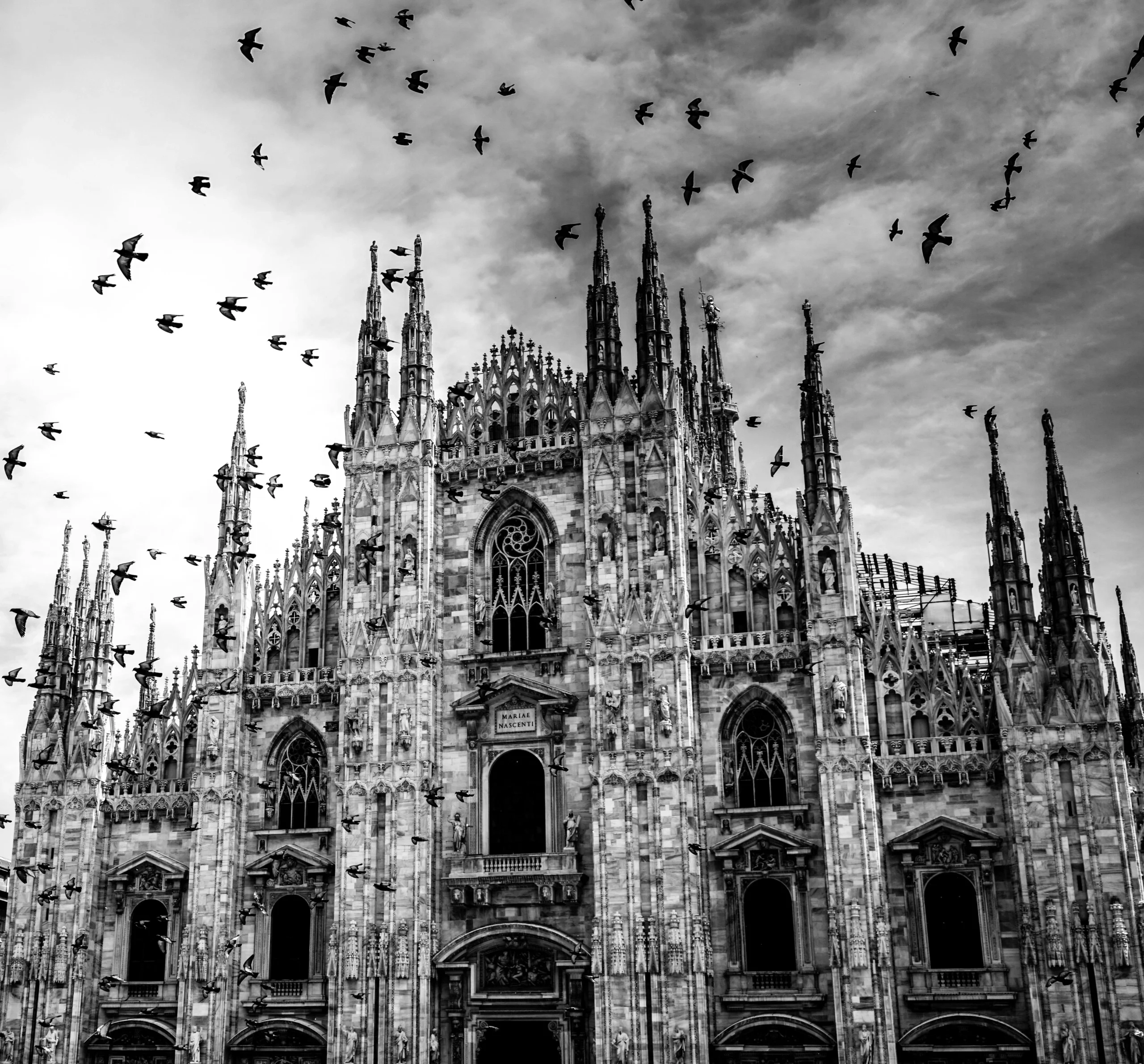
Put simply, Gothic architecture is a striking and graceful building style that originated in medieval Europe. It’s known for its height, pointed arches, detailed facades, and stunning stained glass. But it wasn’t just about creating buildings, it was about reaching toward the heavens and expressing beauty through structure.
Common Misconceptions often confuse the style:
- It’s not only dark and moody — Gothic architecture is actually filled with light, thanks to expansive stained-glass windows.
- It’s not exclusive to churches — castles, universities, and even private homes embraced the Gothic look.
- It isn’t related to modern “goth” fashion — the architectural style predates it by centuries.
Key Features of Gothic Architecture You’ll Recognize
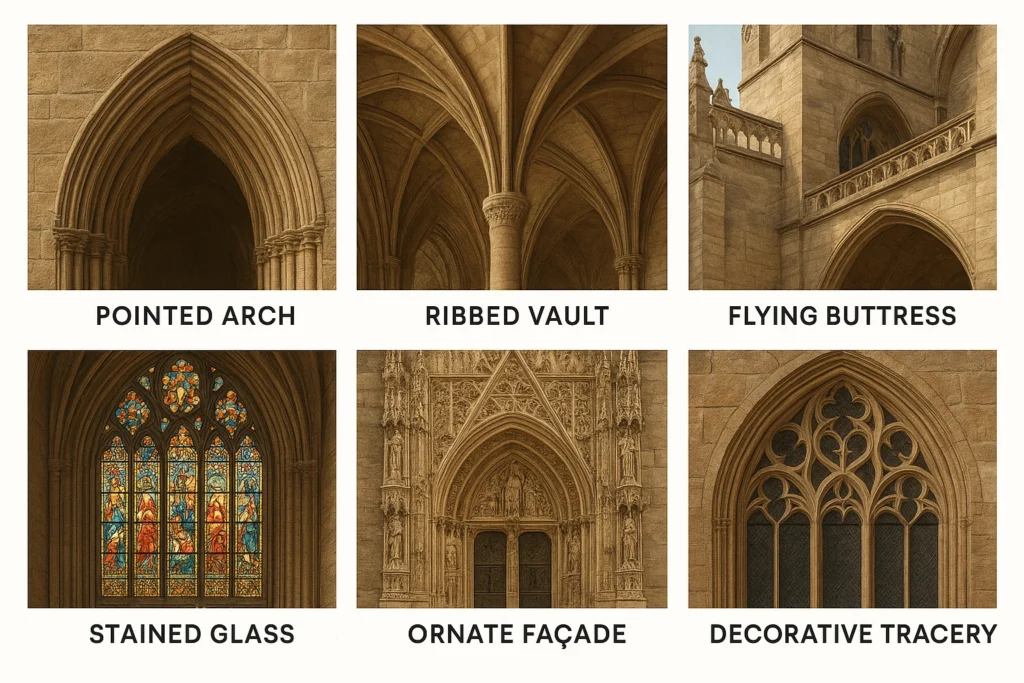
If you’ve admired an old cathedral or seen images of grand European landmarks, you’ve likely noticed certain hallmarks of Gothic style.
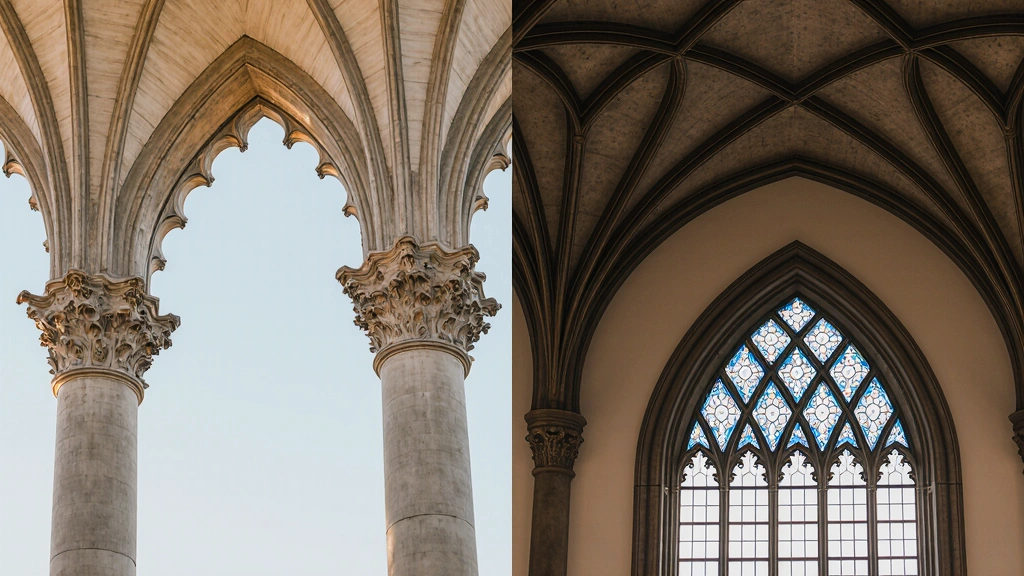
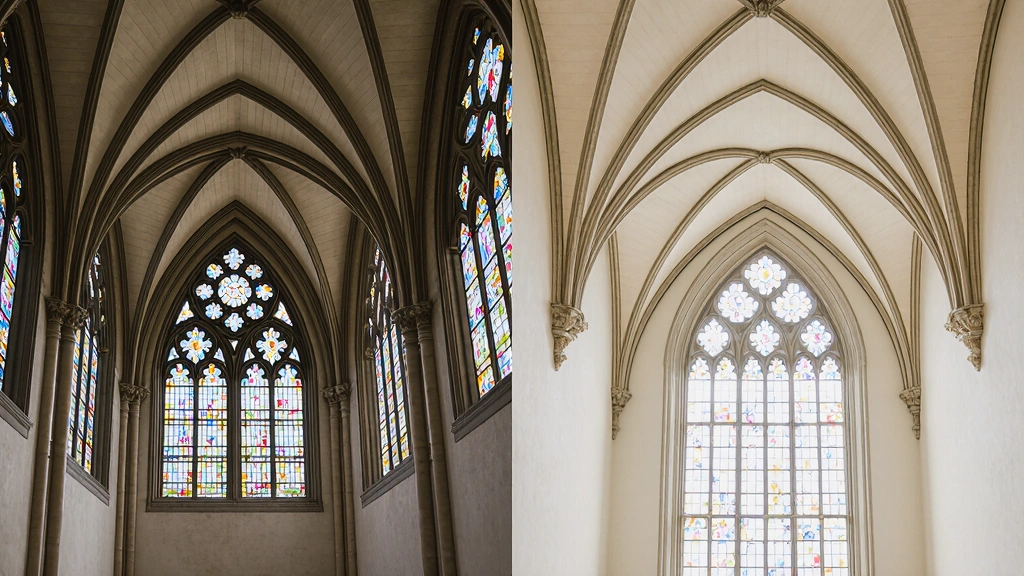
The most recognizable features include pointed arches, which frame doorways and windows with elegance, and ribbed vaults, which turn ceilings into stone patterns that seem to stretch endlessly upward. Flying buttresses stand proudly outside, not only supporting the structure but allowing for breathtaking height. And then, of course, there’s the stained glass windows, filling interiors with dazzling color and biblical stories. Finally, you’ll often see ornate facades and decorative tracery, both of which showcase artistry in stone and wood.
- Pointed arches — Strong, graceful arches framing doors, windows, and walkways.
- Ribbed vaults — Ceilings with exposed rib-like stone patterns.
- Flying buttresses — Exterior supports that made it possible to build taller, more open structures.
- Stained glass windows — Intricate, colorful glass telling biblical stories or adding vibrant light.
- Tall, ornate facades — Dramatic entrances covered in sculpted detail.
- Decorative tracery — Intricate stone or woodwork that creates delicate, lace-like patterns
Quick Comparison of Gothic Features and Modern Interpretations
| Gothic Feature | Original Use | Modern Interior Inspiration |
| Pointed Arches | Structural & Decorative | Archways, Mirrors, Headboards |
| Stained Glass Windows | Religious Symbolism | Colored Glass Decor, Room Dividers |
| Vaulted Ceilings | Grandeur & Space | High Ceilings, Faux Beams |
| Ornamental Details | Visual Storytelling | Moldings, Wall Panels, Artwork |


Where Did Gothic Architecture Begin?
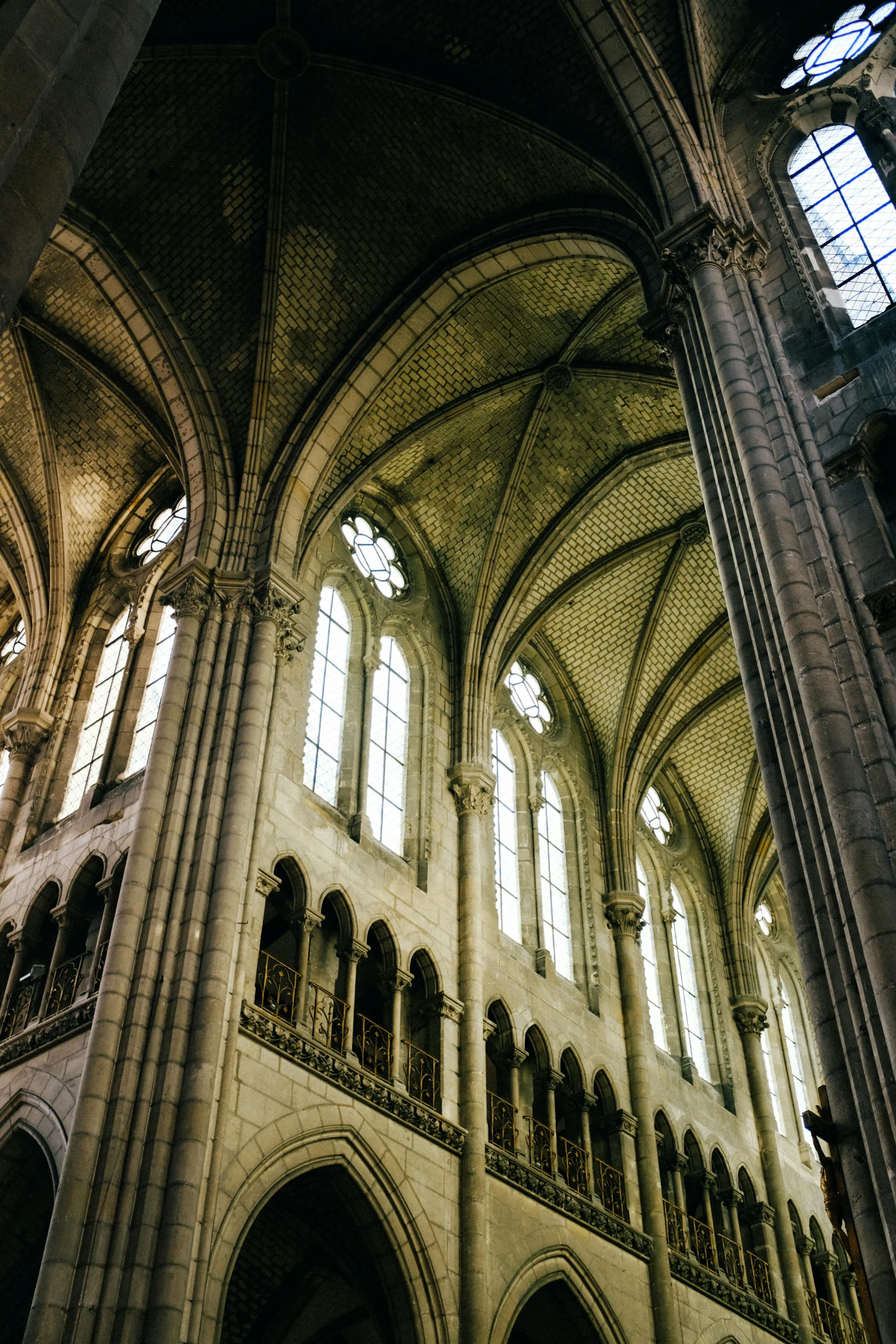

The Birthplace of Gothic Style Architecture
The story of Gothic architecture begins in 12th-century France, at the Abbey of Saint-Denis, just outside Paris. Abbot Suger, the abbey’s visionary leader, dreamed of a church filled with divine beauty and light. By experimenting with new structural techniques, he gave birth to the world’s first true Gothic building.
How It Spread Across Europe
Once the innovation was unveiled, Gothic architecture spread rapidly. In England, Westminster Abbey became a prime example. In Germany, Cologne Cathedral showcased soaring spires. In Italy, the Gothic spirit blended with Italian artistry in Milan Cathedral, while Spain developed its own intricate variations, such as Burgos Cathedral.
Gothic architecture became popular because it allowed builders to create taller and more awe-inspiring structures than ever before. The use of light-filled interiors gave these spaces a spiritual and ethereal quality that drew people in. At the same time, technological innovations such as the flying buttress made these ambitious designs possible, pushing the boundaries of what architecture could achieve.
Early examples beyond France: Canterbury Cathedral (England), Burgos Cathedral (Spain).
What Era is Gothic Architecture From?
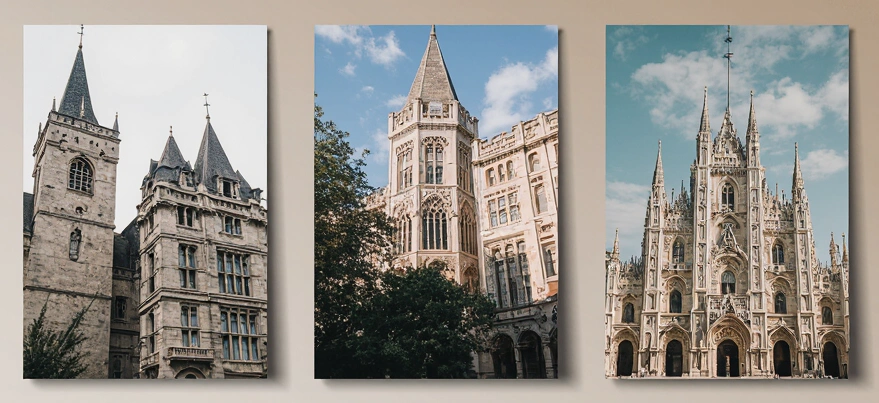

The Gothic Age — A Timeline
When asking what era Gothic architecture belongs to, picture the grandeur of medieval Europe from the 12th to the 16th century. This period, often called the Gothic Age, overlapped with the High and Late Middle Ages and even brushed against the early Renaissance.
Gothic Architecture Through the Centuries
- Early Gothic (12th–13th century): Simple yet groundbreaking, with height and light as key innovations. Examples include the Abbey of Saint-Denis and Notre-Dame de Paris.
- High Gothic (13th–14th century): Cathedrals reached peak complexity and beauty, such as Chartres Cathedral and Amiens Cathedral.
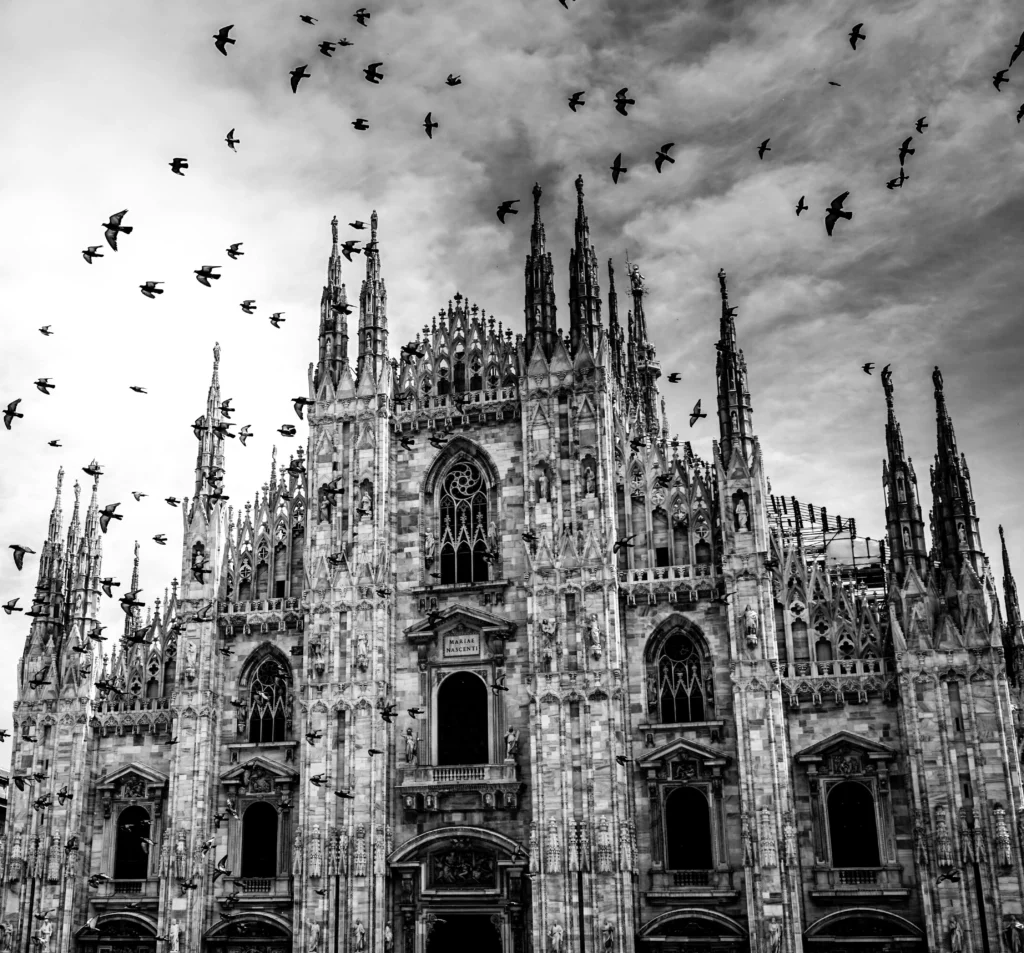
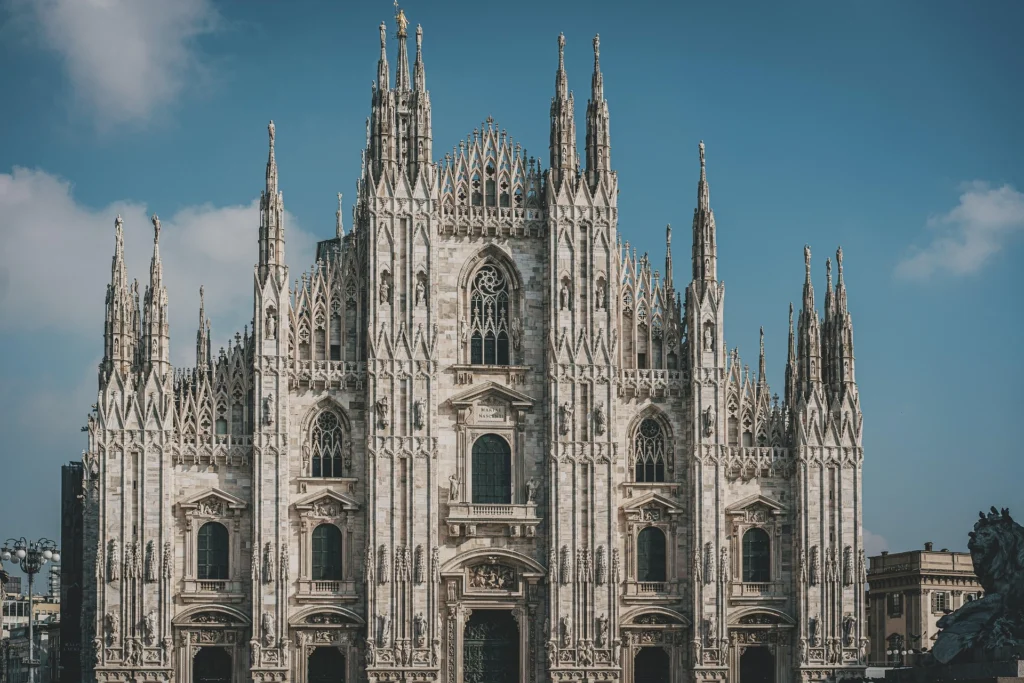
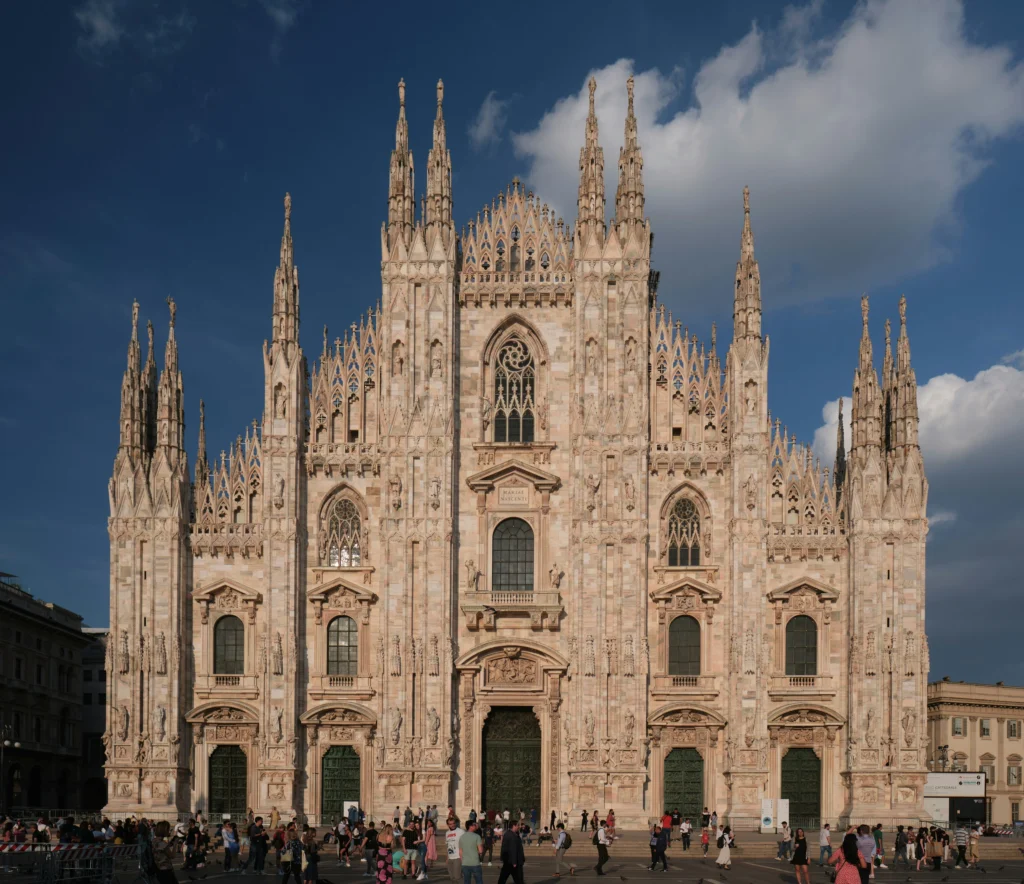
- Late Gothic (14th–16th century): Known as Flamboyant Gothic, this phase emphasized ornate, decorative detail, seen in Milan Cathedral and Rouen Cathedral.
Why Gothic Era Architecture Still Inspires Today
Timeless Beauty Meets Modern Design
The grandeur of Gothic architecture never truly faded. In fact, many design enthusiasts rediscover its beauty through modern interpretations. Dramatic arches add bold focal points, intricate details lend historic elegance, and dark, moody palettes create cozy yet regal interiors. Even in contemporary spaces, arched doorways or high ceilings can echo Gothic grandeur.
Examples of Gothic Influence in Modern Homes
You don’t need to live in a medieval castle to enjoy Gothic-inspired design. Dark, rich palettes of green, burgundy, and charcoal bring depth, while tall windows and statement arches add sophistication. Decorative paneling or carved ceiling details can introduce texture and timeless charm.
Features of Gothic Architecture You Can Bring Into Your Home
Simple Decor Ideas Inspired by Gothic Style Architecture
Adding Gothic elegance to your home doesn’t require major renovations. Start with smaller touches such as pointed arch mirrors to elongate walls, or faux stained glass panels for a splash of color. Decorative ironwork — from candle holders to wall accents — captures the medieval spirit, while velvet upholstery instantly adds richness. For lighting, medieval-inspired candle holders bring both warmth and atmosphere.
So try these easy ideas:
- Pointed arch mirrors — Create height and architectural interest.
- Faux stained glass panels — Bring vibrant color and old-world charm to your windows.
- Decorative ironwork — Think candle holders, hardware, or wall art.
- Velvet furnishings and drapery — Luxurious, moody fabrics.
- Candle holders with medieval flair — Warm, atmospheric lighting.
Gothic-Inspired Decor Pieces for Your Home
| Item | Style Tip | Where to Use |
| Pointed Arch Mirror | Adds height & elegance | Entryway, Living Room |
| Stained Glass Art Panel | Colorful focal point | Windows, Wall Accents |
| Ornamental Wall Molding | Historical charm | Hallways, Dining Room |
| Gothic Chandelier | Dramatic lighting | Foyer, Dining Area |
| Velvet Upholstery | Luxurious texture | Sofa, Accent Chairs |
Famous Gothic Architecture Landmarks from Around the Globe
Famous Gothic Buildings to Know
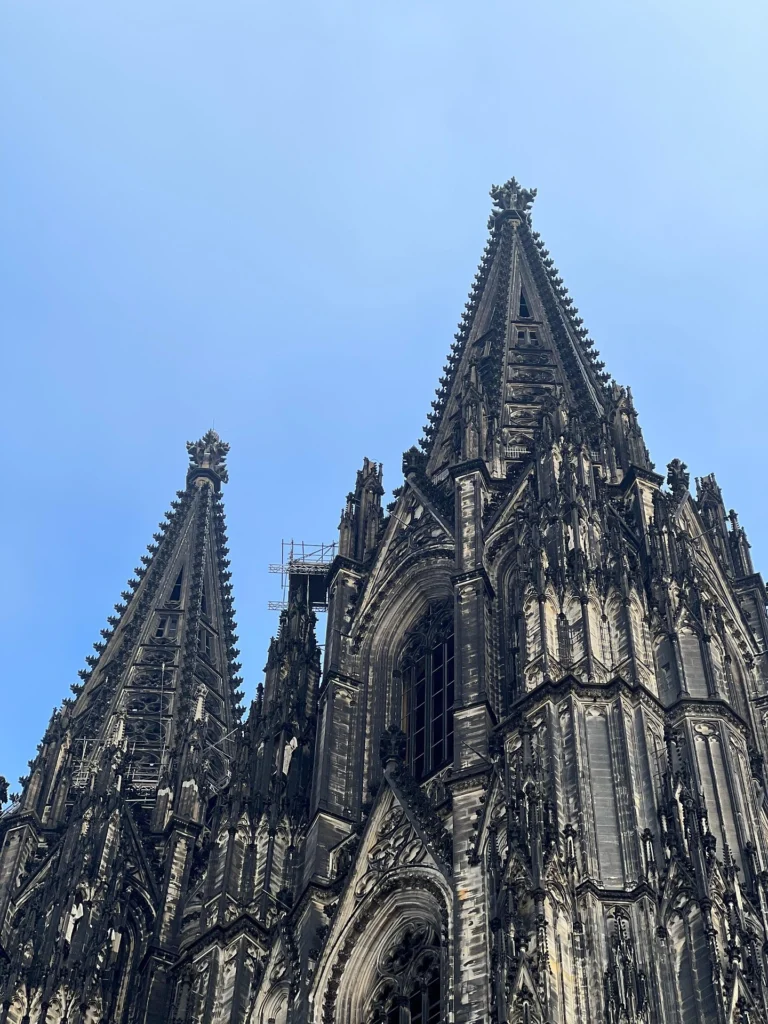
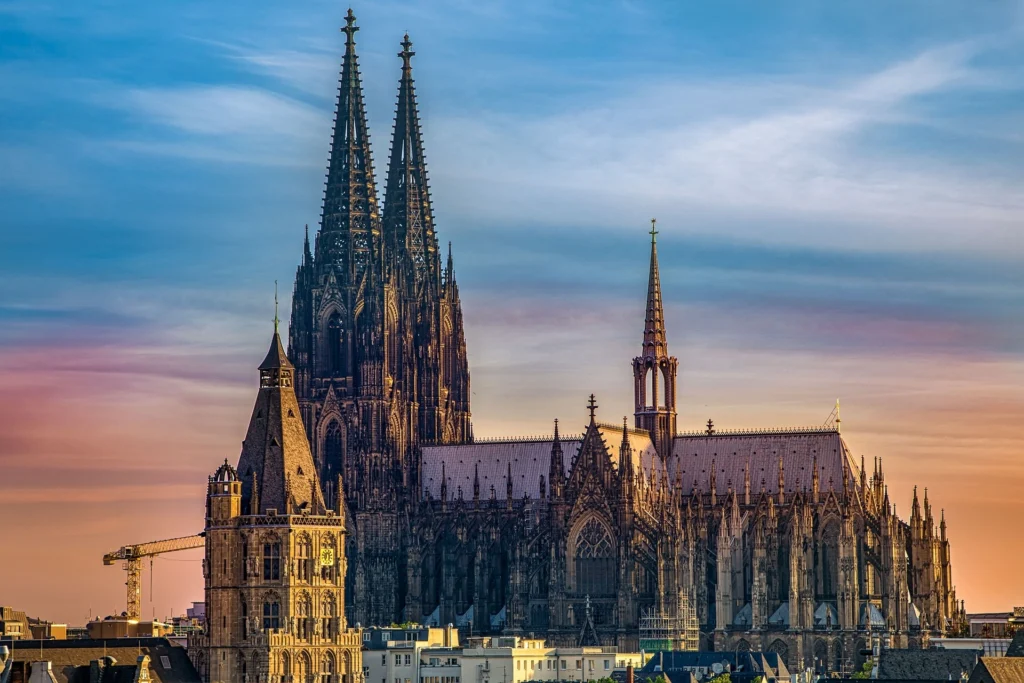
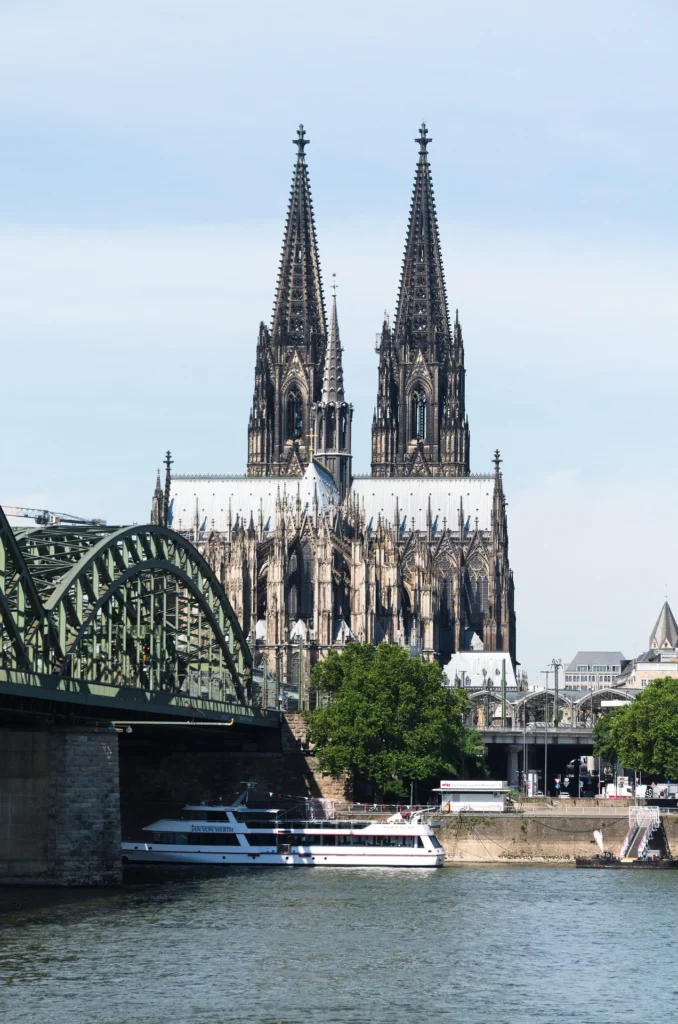
Some of the most iconic landmarks in the world are Gothic masterpieces. Notre-Dame de Paris remains the symbol of Gothic style, while Chartres Cathedral is celebrated for its stained glass. Cologne Cathedral in Germany rises skyward with unmatched power, and Milan Cathedral displays the flamboyant beauty of late Gothic. In England, Westminster Abbey combines architectural splendor with royal history.
Notre-Dame de Paris, France — The quintessential Gothic cathedral.
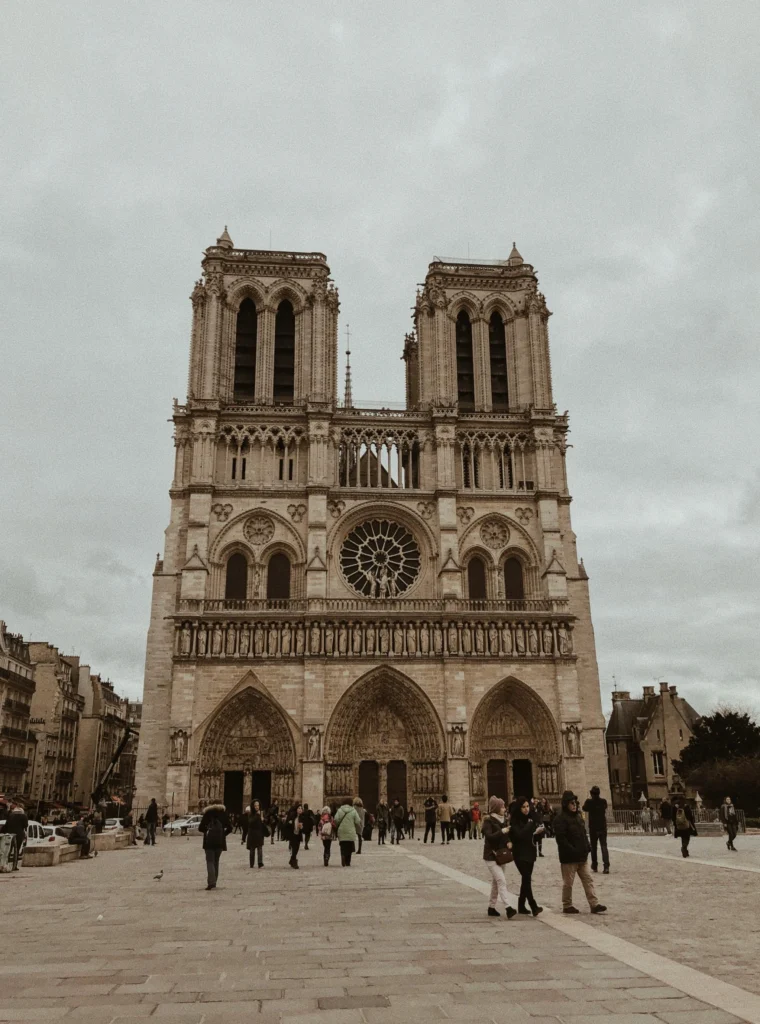
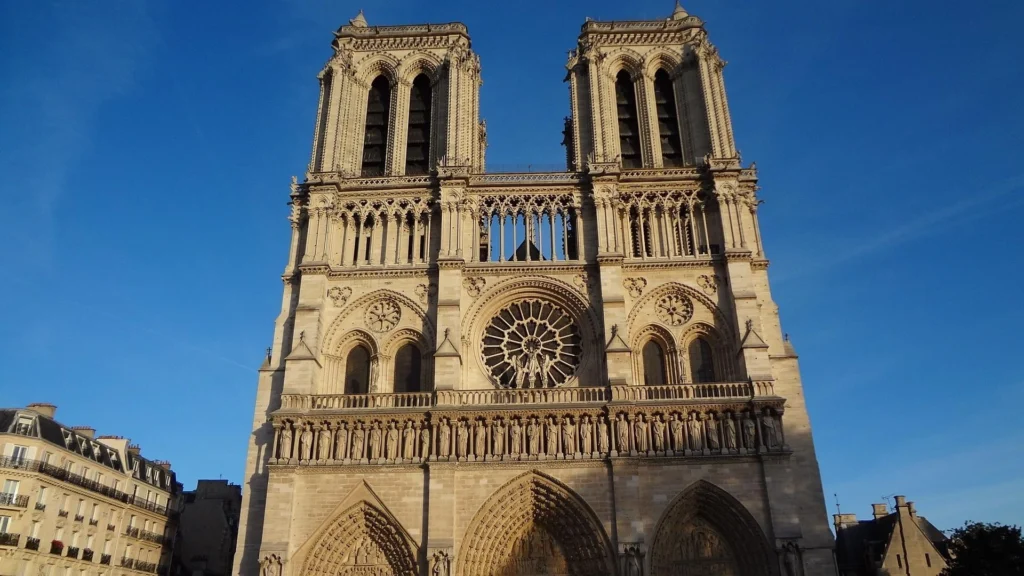
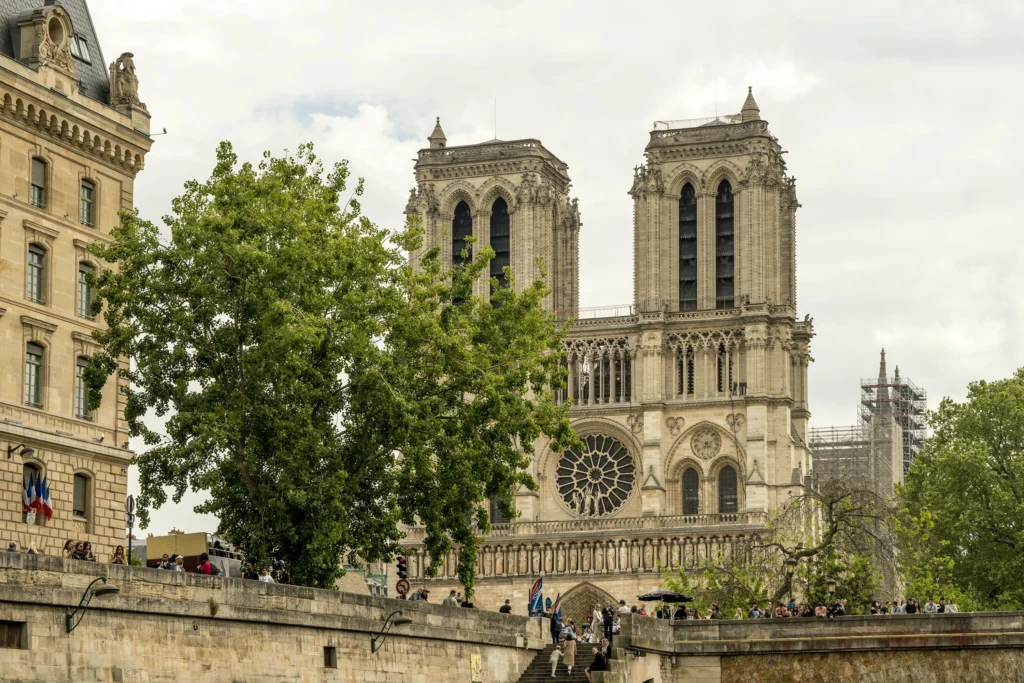



Chartres Cathedral, France — Known for its stunning stained glass.
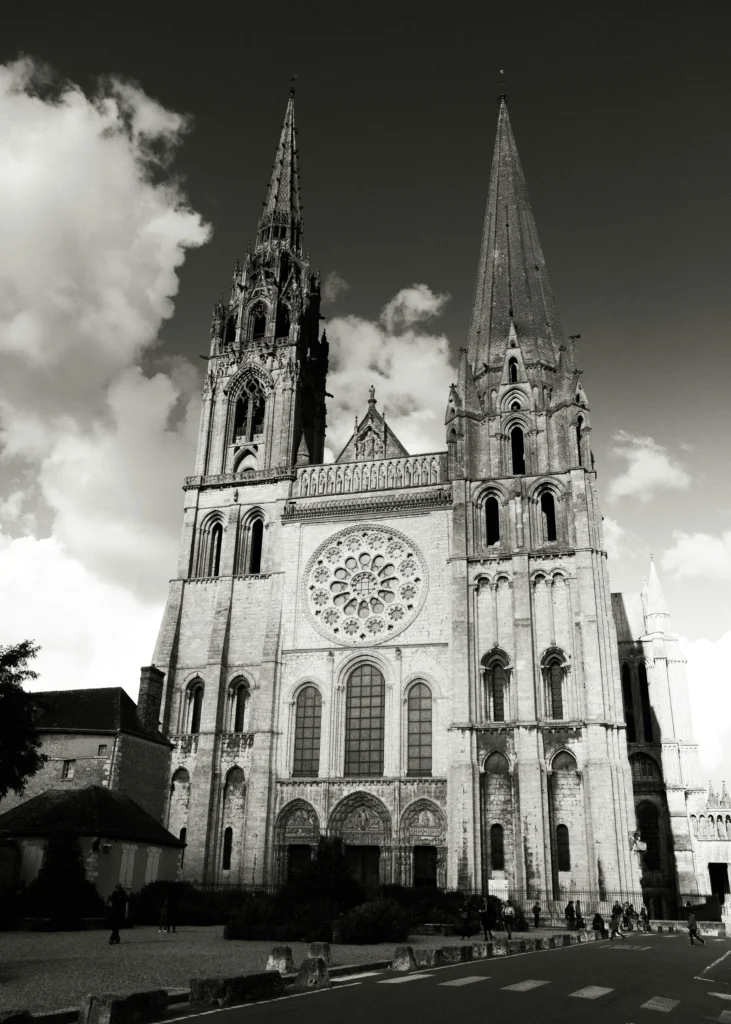
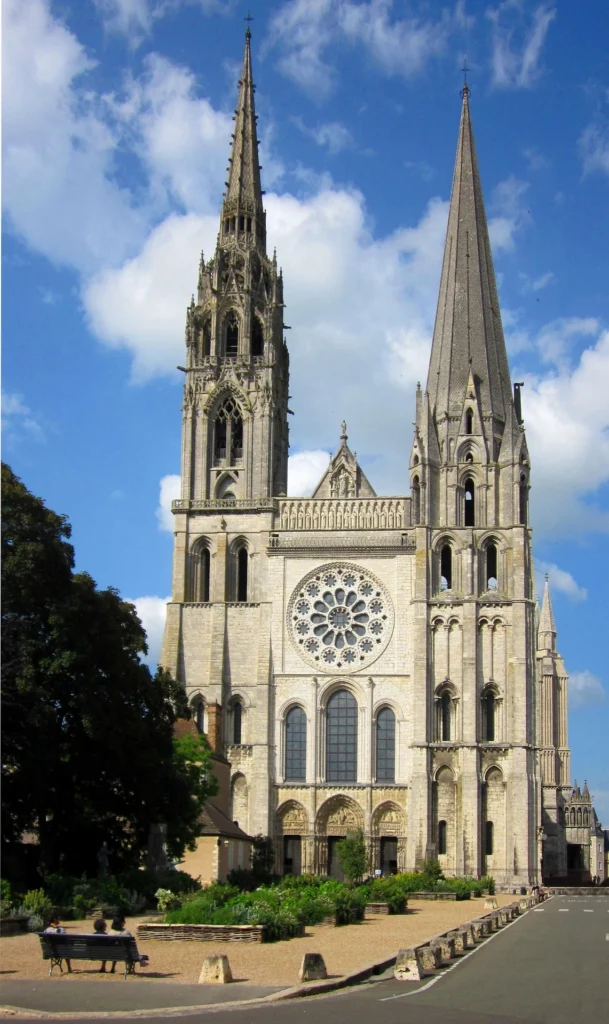
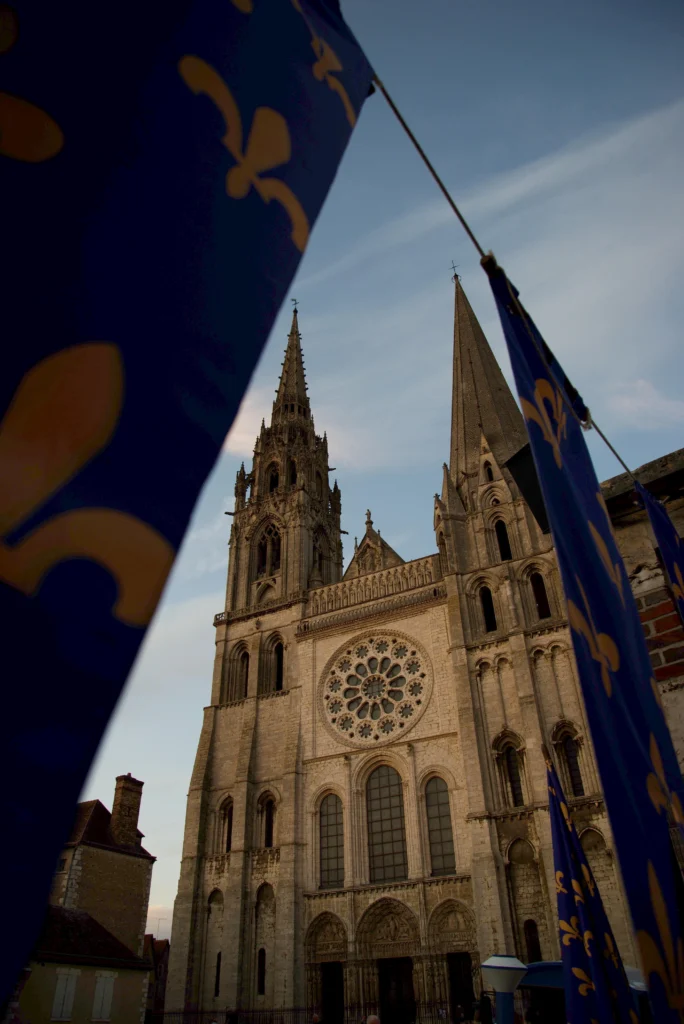



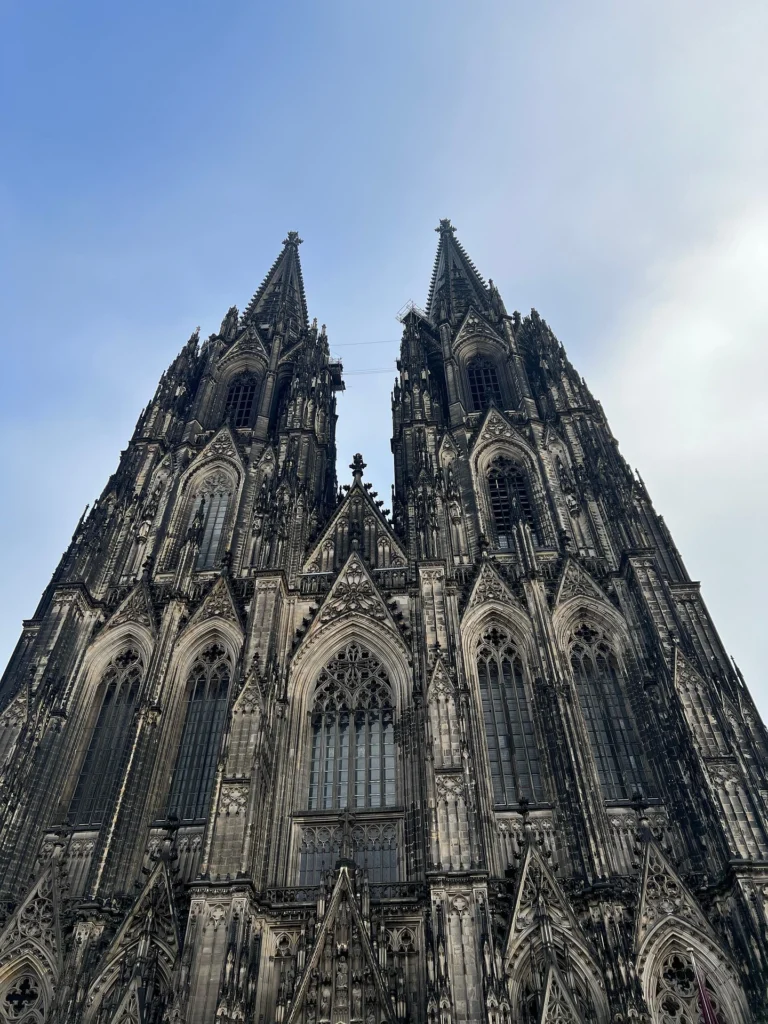
Cologne Cathedral, Germany — Towering spires and awe-inspiring verticality.




Milan Cathedral, Italy — Late Gothic flamboyance at its finest.





Westminster Abbey, England — A royal and historical masterpiece.
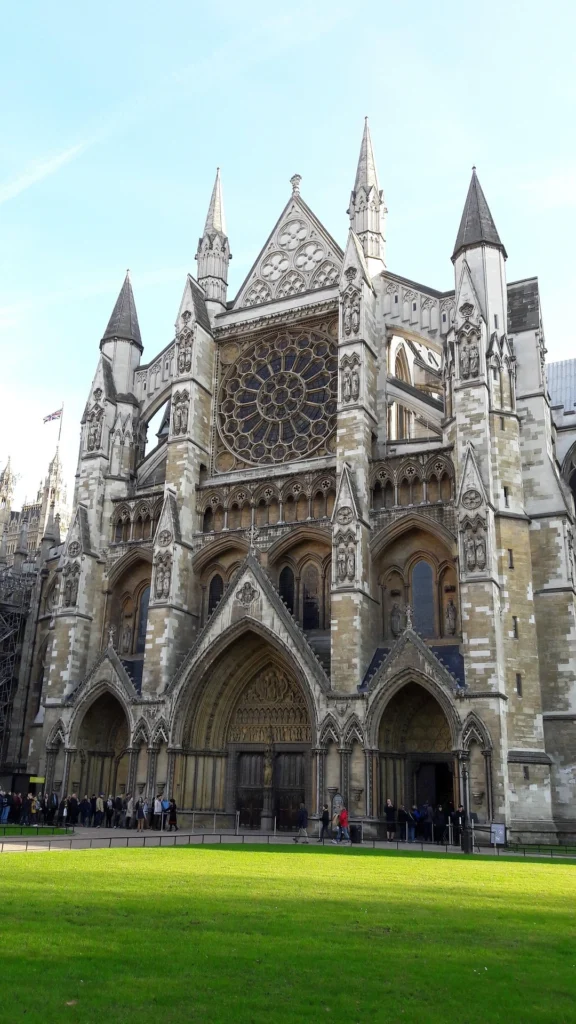
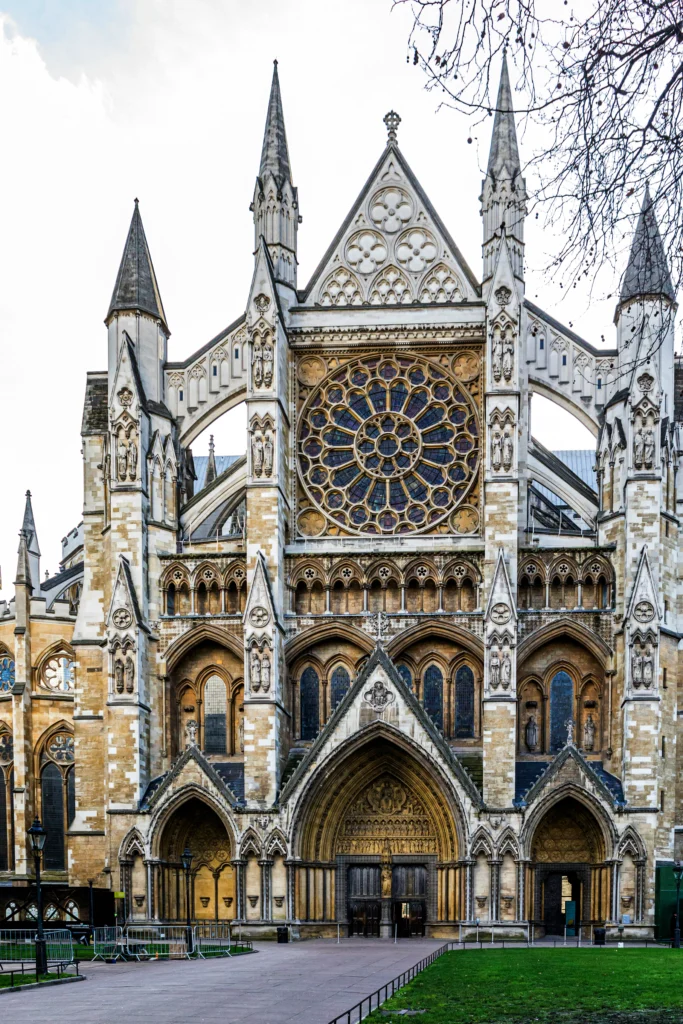
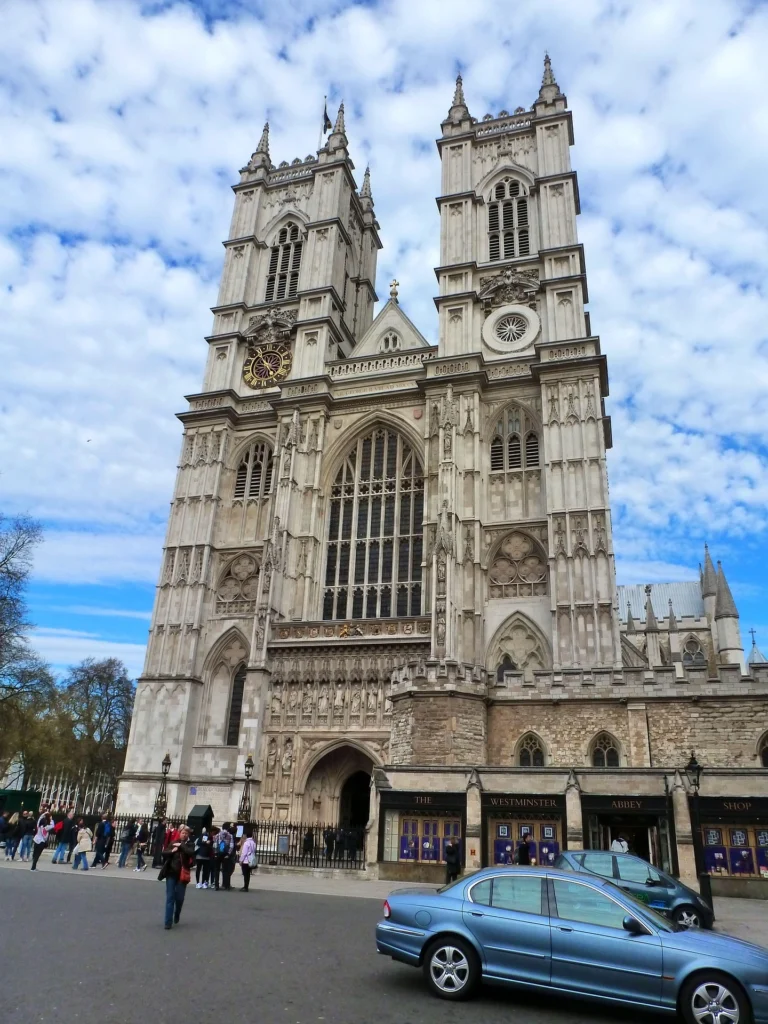
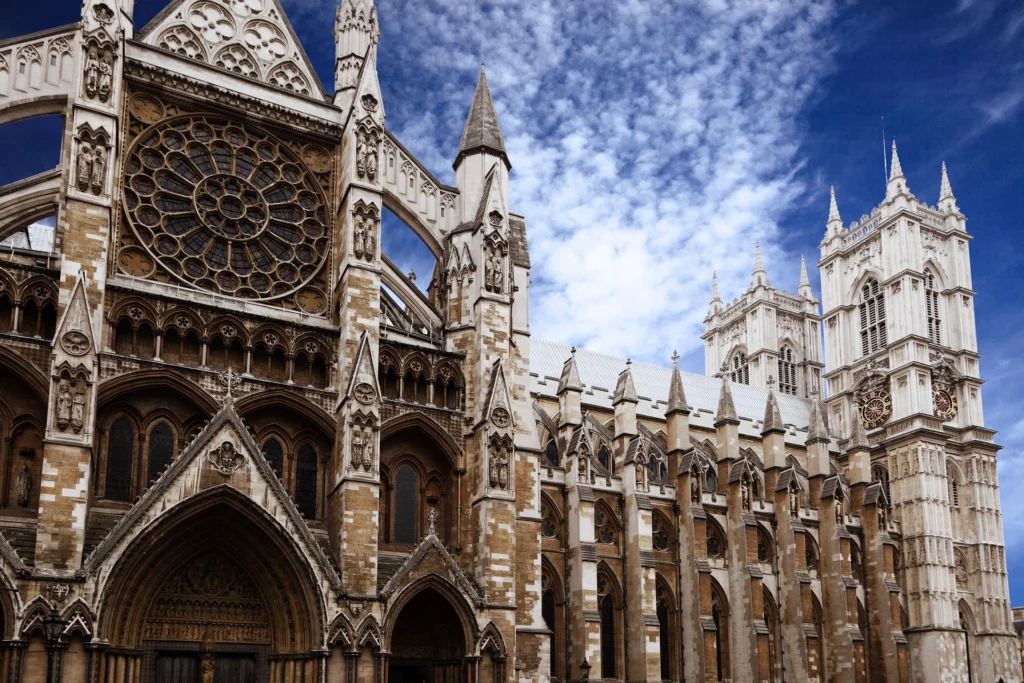




How These Landmarks Shaped Design History
These Gothic landmarks weren’t just architectural feats, they changed the course of design history. Through technological innovations like flying buttresses and ribbed vaults, they redefined what was structurally possible. Their artistic legacy went far beyond architecture, inspiring art, sculpture, and even fashion. Today, their global admiration continues, as tourists and designers alike still flock to these masterpieces to study and be inspired by their grandeur.
Styling Your Space with Gothic Age Inspiration
Tips for Creating a Gothic-Inspired Interior

You can bring Gothic inspiration into your home without overwhelming your space. Begin with a moody, neutral palette in charcoal or navy, then add architectural touches like arched mirrors or wall panels. Layer rich fabrics such as velvet or brocade for depth, and focus on dramatic lighting with chandeliers or sconces. Finally, add historic accents like vintage frames or replica pieces.
Here’s how (Notes):
- Start with a moody, neutral palette — Deep grays, charcoals, navy.
- Add structural elements — Arches, pointed mirrors, wall panels.
- Incorporate rich fabrics — Velvet, brocade, heavy drapery.
- Focus on dramatic lighting — Gothic-style chandeliers, candle sconces.
- Use historical accents — Vintage pieces, replica decor, intricate frames.




Do’s and Don’ts for Gothic-Inspired Decor
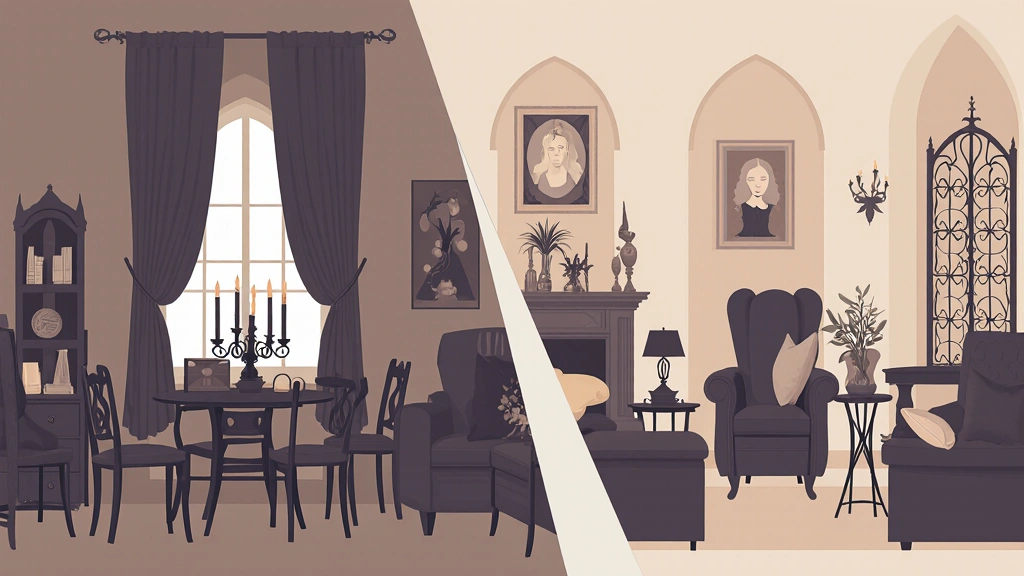

✅ Do:
- Mix old-world charm with modern comfort.
- Use dark tones thoughtfully to keep balance.
- Highlight unique architectural details.
🚫 Don’t:
- Crowd the space with bulky furniture.
- Make everything overly dark.
- Forget to personalize with items that reflect you.

Conclusion — Gothic Architecture’s Enduring Beauty
Whether you admire grand cathedrals or simply want to add a touch of historic drama to your home, Gothic architecture continues to inspire. From its French beginnings to its worldwide influence, its elegance, detail, and unmistakable drama have left a lasting mark. With just a few thoughtful choices, you can bring echoes of this timeless style into your own living space.
Key Takeaways
- Gothic architecture originated in 12th-century France before spreading across Europe.
- It belongs to the Gothic Age, spanning the High and Late Middle Ages.
- Defining features include pointed arches, ribbed vaults, stained glass, and ornate facades.
- Modern design often borrows from Gothic style for elegance and drama.
- You can incorporate subtle Gothic elements into your home for a bold yet timeless look.
FAQ — Your Gothic Architecture Questions Answered
- Where did Gothic architecture originate?
It began in France, particularly at the Abbey of Saint-Denis near Paris in the 12th century. - What era is Gothic architecture from?
The Gothic Age, spanning from the 12th to the 16th century, overlapping with the Middle Ages. - What are the key characteristics of Gothic architecture?
Pointed arches, ribbed vaults, flying buttresses, stained glass windows, and elaborate facades. - Can I incorporate Gothic style into modern home decor?
Absolutely! Mirrors, arches, rich fabrics, and dramatic lighting are easy ways to do so. - Why is Gothic architecture still admired today?
Its dramatic beauty, technical achievements, and ability to inspire awe make it timeless.
Ready to bring Gothic-inspired beauty into your home? Begin with subtle decor accents, or go bold with major structural updates. Either way, the bold elegance of Gothic architecture is yours to enjoy.