Architecture vs. Architectural Engineering: What’s the Difference?
Table of Contents
Introduction to Architecture and Architectural Engineering

Understanding the Purpose of This Comparison

Understanding the difference between architecture and architectural engineering is essential for students considering a career in the built environment, homeowners looking to renovate or build, and professionals seeking clarity between disciplines. Although these two fields often collaborate on the same projects, their core purposes, educational paths, and job roles are fundamentally different.

Confusion often arises due to overlapping terminology. For instance, an “engineer architect” is not a formal title in the U.S., yet many assume the roles are interchangeable. This article demystifies these professions and explains their unique contributions to the built world.
Defining the Main Keyword
While architecture and architectural engineering are both vital to the construction process, they approach the built environment from different perspectives. Architecture focuses on spatial aesthetics, cultural context, and the user experience of space. In comparison, architectural engineering focuses on structural stability, building systems, and overall technical efficiency.
What Is Architecture?

Core Concepts and Design Philosophy

Architecture blends art and science to design spaces that are functional, safe, and visually appealing. At its core, it involves:
- Designing environments that reflect cultural identity
- Balancing beauty, function, and sustainability
- Exploring human interaction with space
An architect considers form, proportion, light, material, and context. The result is a structure that transcends utility and becomes part of the human experience.
Historical Development of Architecture

Architecture has evolved over thousands of years:
- Ancient Civilizations: Structures like Egyptian pyramids, Mesopotamian ziggurats, and Greek temples emphasized symbolic meaning and architectural order.
- Roman Empire: Introduced arches, aqueducts, and concrete, enabling large-scale public architecture.
- Medieval Era: Gothic cathedrals showcased verticality, stained glass, and flying buttresses.
- Renaissance: Revival of classical ideals, with emphasis on symmetry, geometry, and perspective.
- Modernism: Originated in the early 20th century through movements like Bauhaus and the International Style, emphasizing functionality and minimal design.
- Postmodern and Deconstructivism: Challenged modernist ideals, embracing complexity and fragmentation.
The Architect’s Role

Architects conceptualize spaces and transform ideas into detailed plans. Their responsibilities include:
- Meeting with clients to define project goals
- Creating floor plans, elevations, and site designs
- Making sure designs follow zoning regulations and building codes
- Coordinating with engineers, planners, and contractors
Their creative vision guides the project’s overall direction.
Skills Required in Architecture

Successful architects blend creativity with technical skill. Key competencies include:
- Artistic visualization and drawing
- Deep understanding of historical and modern styles
- Skilled in CAD and BIM tools such as AutoCAD and Revit
- Strong communication and project management
What Is Architectural Engineering?
Definition and Scope
Architectural engineering is a branch of engineering dedicated to the design and analysis of building systems. It includes:
- Structural systems: Beams, columns, load-bearing frameworks
- Mechanical systems: HVAC, plumbing
- Electrical systems: Lighting, power distribution
- Environmental systems: Energy modeling, water efficiency

While architects focus on “what” a space will be, architectural engineers determine “how” it can be safely and efficiently built.
Historical Emergence
The profession emerged during the Industrial Revolution, when construction complexity outpaced the traditional architect’s technical knowledge. By the late 1800s and early 1900s, architectural engineering had developed into a recognized and separate discipline.
- ABET (Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology) began accrediting architectural engineering programs in the U.S. in the 20th century.
- The need for specialized engineers grew with the rise of skyscrapers, complex HVAC systems, and energy regulations.
Architectural Engineer Job Description

An architectural engineer plays a crucial role in system integration and safety. Core responsibilities include:
- Designing HVAC, lighting, fire safety, and structural systems
- Conducting energy efficiency assessments
- Analyzing loads, materials, and environmental impacts
- Verifying adherence to local and national building regulations
Skills and Educational Requirements

Unlike architecture, architectural engineering demands a solid foundation in STEM:
- Proficiency in calculus, physics, structural mechanics
- Familiarity with simulation tools like MATLAB, Revit MEP, and SAP2000
- A typical academic path involves a B.S. in Architectural Engineering
- Obtaining a license requires passing the FE (Fundamentals of Engineering) and PE (Professional Engineer) examinations
What Does an Architectural Engineer Do in Practice?
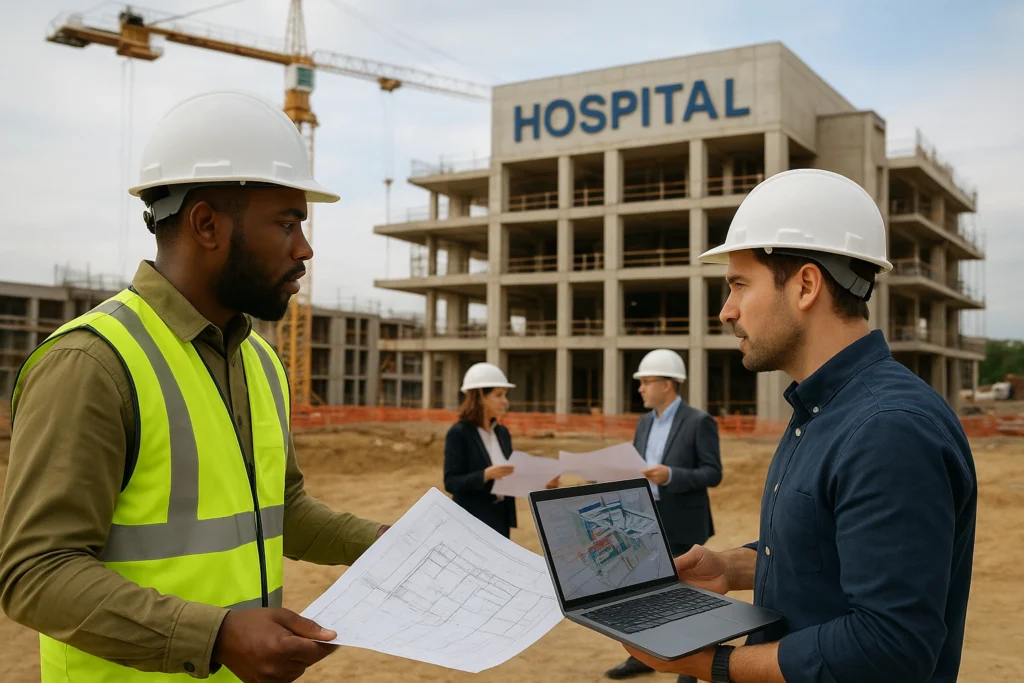

Architectural engineers bridge the gap between architectural design and construction execution. In practice, they:
- Collaborate with architects and civil engineers
- Optimize systems for safety, efficiency, and cost
- Work on diverse projects: hospitals, stadiums, office buildings
For example, designing a hospital may involve complex mechanical systems for airflow, which falls under the engineer’s domain.
Architecture vs. Architectural Engineering: A Detailed Comparison

Key Differences in Focus
| Aspect | Architecture | Architectural Engineering |
| Primary Focus | Aesthetics, form, space | Building systems, structure |
| Perspective | Conceptual, artistic | Analytical, technical |
| Outcome | Building appearance & experience | Building safety & functionality |
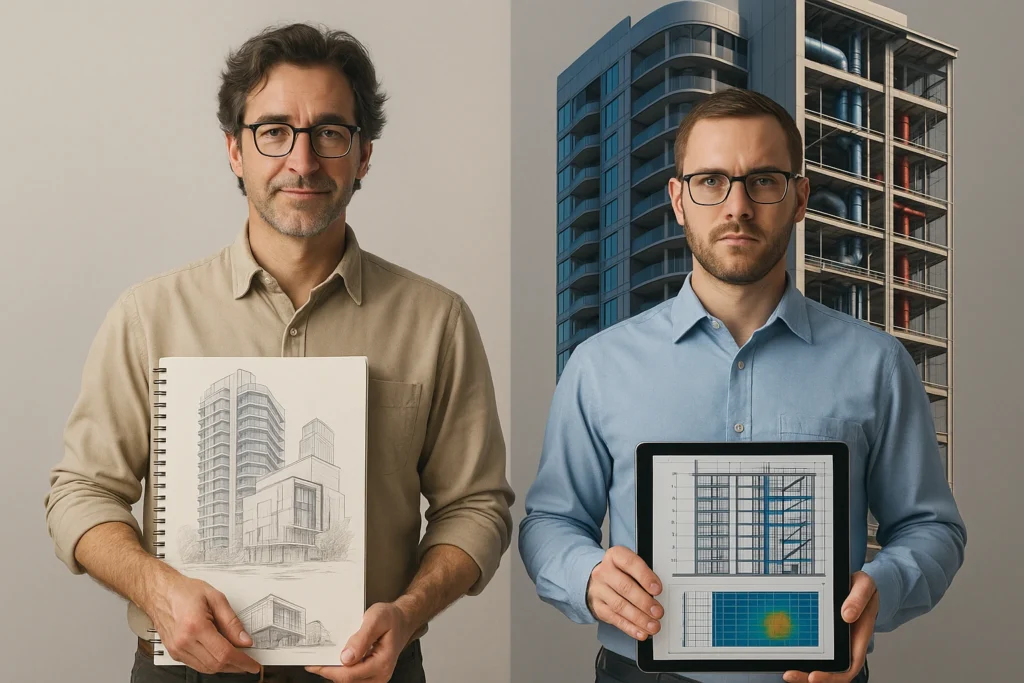

Education and Training
- Architecture: Involves B.Arch or M.Arch degrees. Requires internship and the Architect Registration Exam (ARE).
- Architectural Engineering: Involves a B.S. in Architectural Engineering. Requires PE licensure for practice.
Career Paths and Salaries

- Architects: Residential, commercial, urban design
- Architectural Engineers: MEP design, structural analysis, energy modeling
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS):
- Median salary (2023):
- Architect: ~$89,000
- Architectural Engineer: ~$95,000
- Architect: ~$89,000
- Job growth (2022–2032):
- Architecture: 5%
- Architectural Engineering: 8%
- Architecture: 5%
Design Tools and Technology
- Architects: AutoCAD, Revit, Rhino, SketchUp
- Engineers: AutoCAD MEP, MATLAB, Revit MEP, SAP2000
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
On major building projects, both professionals collaborate extensively. For instance:
- The architect defines the building’s form
- The engineer ensures that the form is structurally sound, well-ventilated, and energy efficient
Landmark projects such as the Burj Khalifa and One World Trade Center highlight the power of effective collaboration.
Comparative Table
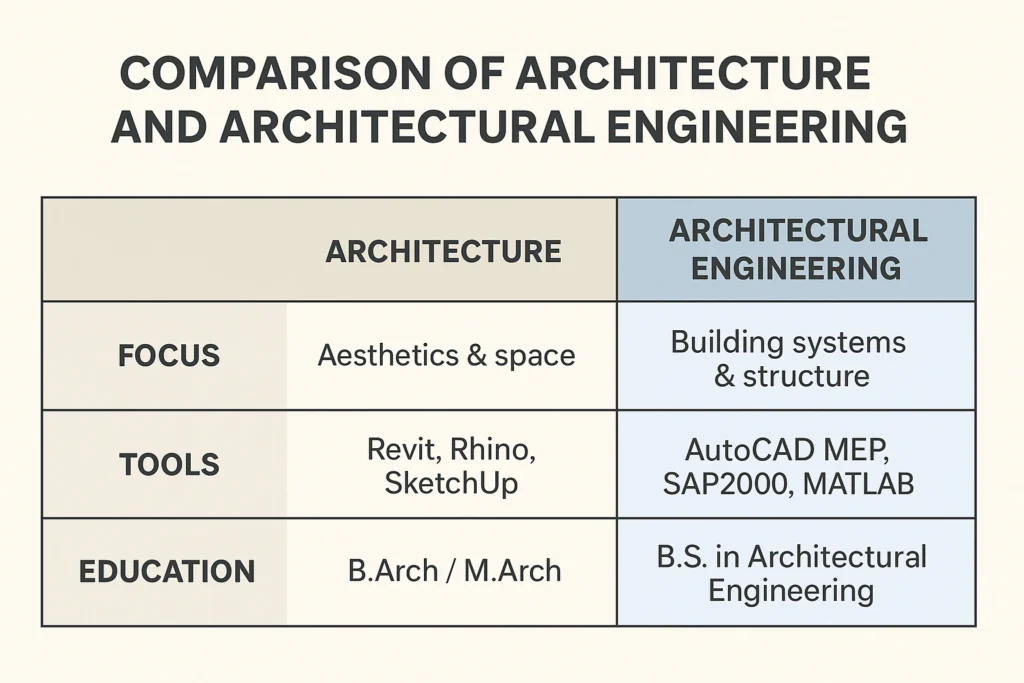
| Feature | Architecture | Architectural Engineering |
| Focus | Aesthetics & space | Building systems & structure |
| Education | B.Arch / M.Arch | B.S. Arch Eng. |
| Tools | Revit, Rhino, SketchUp | AutoCAD MEP, SAP2000, MATLAB |
| Outcome | Building perforBuilding formmance | |
| Licensure | ARE | PE License |
Real-World Impact of Both Fields

Iconic Projects Shaped by Both Disciplines
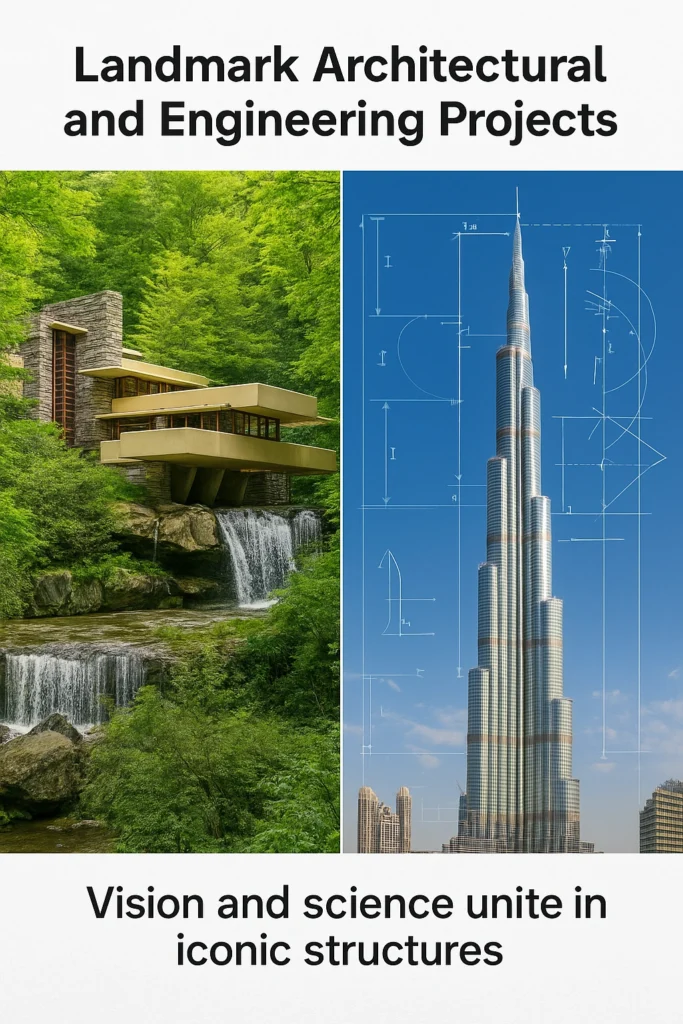

- Fallingwater (Frank Lloyd Wright): Architect-led vision that harmonizes with nature.
- The Burj Khalifa: Collaborative achievement integrating complex structural systems.
Sustainability and Innovation
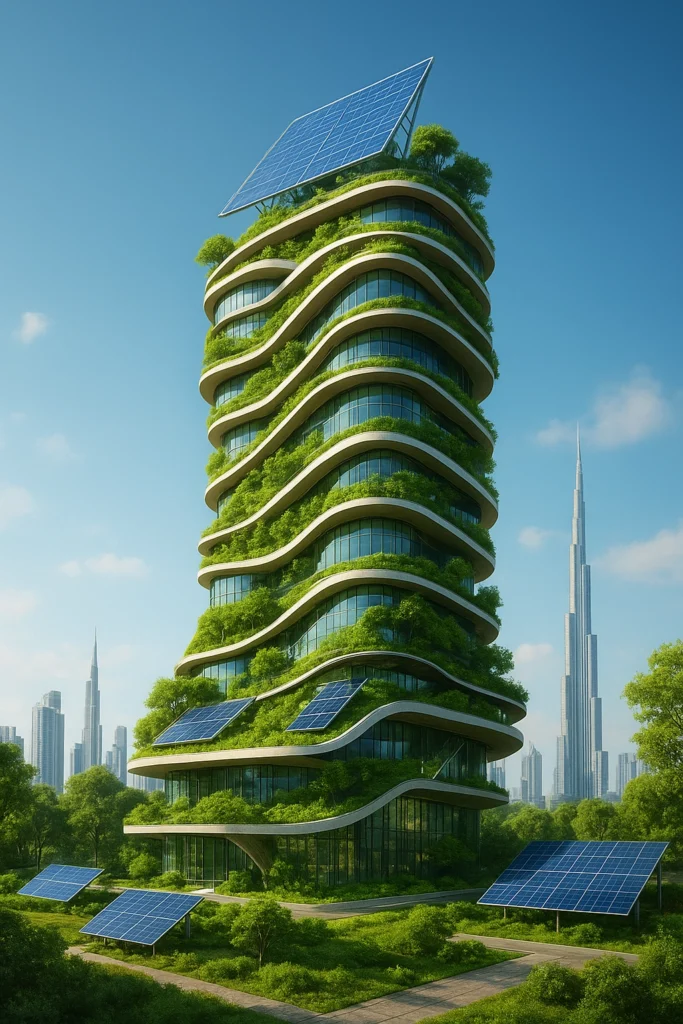

- Architects and engineers collaborate on green buildings and LEED-certified projects.
- Engineers model energy efficiency and airflow; architects choose materials and orientation.
Challenges and Future Trends

- Climate-resilient and net-zero design
- AI-driven design simulations and parametric tools
- Integrated smart systems for buildings
Key Historical Figures in Both Fields
Influential Architects

- Frank Lloyd Wright – Organic architecture and modernism
- Le Corbusier – Pioneer of the International Style
- Zaha Hadid – Parametric, deconstructivist designs
Pioneers in Architectural Engineering

- Fazlur Rahman Khan – Revolutionized skyscraper design (tubular systems)
- John Smeaton – A pioneering structural engineer of the 18th century
Education and Career Guidance for Students

Choosing Between Architecture and Architectural Engineering
Consider the following:
- Do you enjoy artistic creativity and spatial storytelling? → Architecture
- Are you drawn to physics, math, and problem-solving? → Architectural Engineering
Accredited U.S. Programs

Top U.S. universities include:
- Architecture: MIT, Harvard, Columbia, USC
- Top Architectural Engineering Programs: Penn State, University of Texas at Austin, and Kansas State University
Career Advancement Opportunities
- Architects can become lead designers, firm partners, or urban planners
- Engineers can become project managers, sustainability consultants, or lead engineers
- Continuing education includes certifications in BIM, LEED, and project management
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the difference between architecture and architecture engineering?
Architecture focuses on design, form, and aesthetics; architectural engineering focuses on structural systems and technical performance.
Can an architect become an architectural engineer?
While possible through additional education, the fields require distinct licenses and training. Most professionals specialize in one.
Is architectural engineering harder than architecture?
Both are challenging in different ways. Architecture leans on creativity; architectural engineering requires advanced math and physics.
Who earns more — an architect or an architectural engineer?
According to BLS data, architectural engineers tend to earn slightly more, depending on specialization and region.
Do both professions require licensure in the U.S.?
Yes. Architects must pass the ARE, and engineers need PE licensure.
How do architecture and engineering overlap in modern practice?
Collaboration is critical. Engineers make architects’ visions structurally feasible and energy efficient.
Conclusion

Summary of Core Differences
Architecture and architectural engineering share a common goal: shaping the built environment. However, they approach it from different angles—artistic versus technical, conceptual versus analytical. Understanding their distinctions helps clarify career paths and project roles.
Final Thoughts for Aspiring Professionals

If you’re passionate about buildings and how people interact with them, both paths offer rewarding careers. Whether you’re drawn to design narratives or technical systems, your work will help define the future of our cities, homes, and public spaces.