Understanding Architectural Plans: Basics for Homeowners

Table of Contents
Introduction to Architectural Plans
What Is an Architectural Plan?
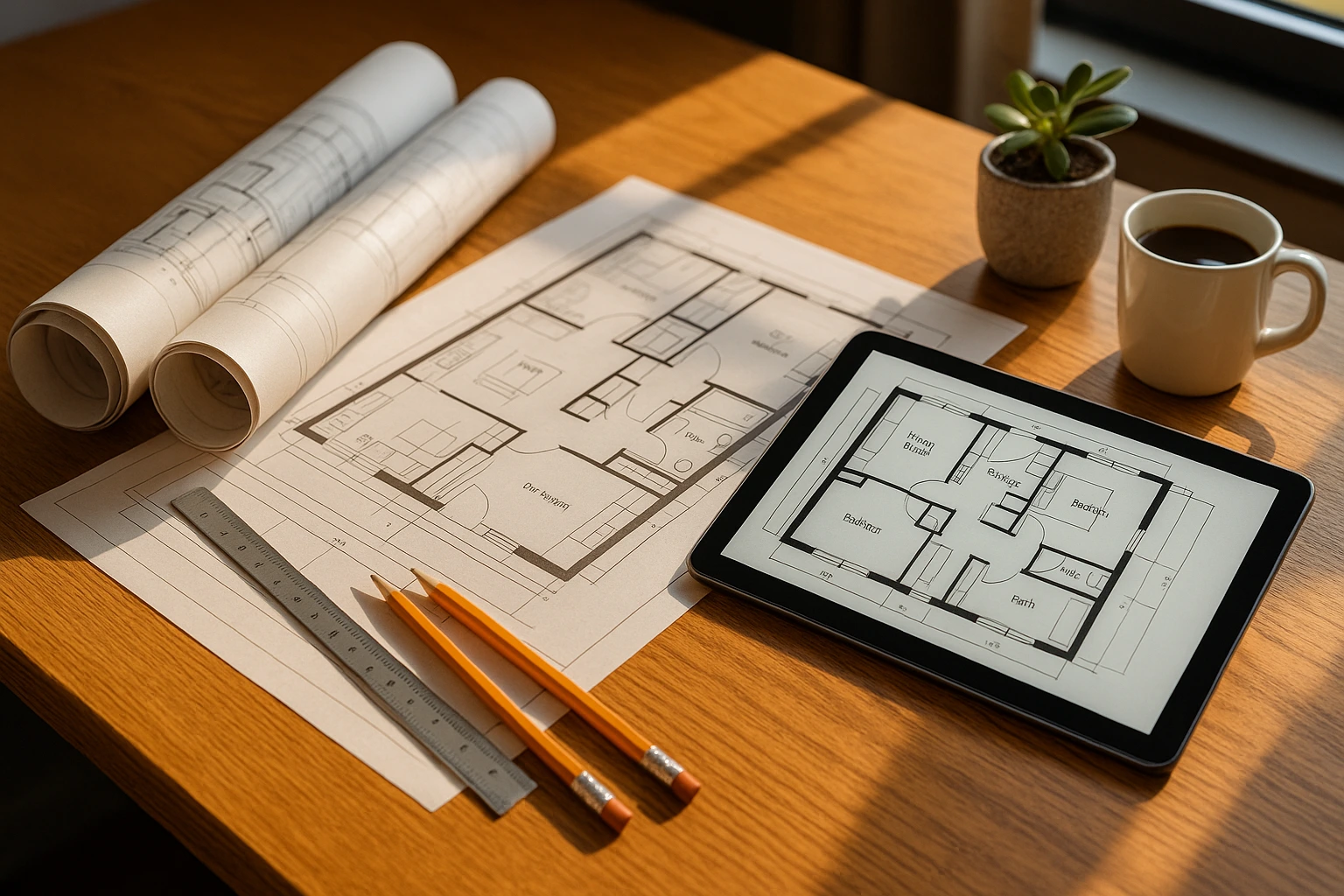
An architectural plan is a detailed, scaled drawing that illustrates the layout, design, and spatial organization of a building or structure. Serving as a visual communication tool, it conveys the architect’s vision and guides contractors through construction. While often used interchangeably with blueprints, the term “blueprint” refers to an older reproduction technique. Today, most plans are created digitally using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software.
Why Homeowners Should Understand Them
Understanding architectural plans is essential for homeowners embarking on renovations, custom builds, or even purchasing property. Misinterpretations can lead to costly errors, timeline delays, or dissatisfaction with the final outcome. With a foundational grasp, homeowners can better collaborate with architects, ask informed questions, and make confident design decisions.
The Evolution of Architectural Drafting
Architectural drafting has transformed significantly, evolving from hand-drawn ink and paper techniques to highly sophisticated digital drafting platforms. CAD software such as AutoCAD and Revit has revolutionized how plans are created, revised, and shared. The rise of online architecture design platforms has also enabled greater access for homeowners to explore and customize home layouts remotely.
A Historical Perspective on Architectural Plans
Ancient and Classical Planning Techniques
Architectural planning dates back millennia. In Ancient Greece and Rome, architecture followed strict proportional rules. Roman architect Vitruvius emphasized symmetry, proportion, and functionality in his influential treatise De Architectura. Greek temples, such as the Parthenon, were laid out using harmonic ratios, reflecting cultural ideals of balance and beauty.
Medieval to Renaissance House Plans
The Gothic period introduced complex layouts for cathedrals and castles, characterized by verticality and intricate spatial arrangements. The Renaissance saw a return to classical balance. Architects like Andrea Palladio produced highly influential residential plans based on symmetry, axial alignments, and mathematical harmony, significantly shaping European and colonial American housing.
Industrial Revolution and Modern Blueprints
The Industrial Revolution emphasized functionality and efficiency, prompting the development of mass-produced housing. With the advent of the blueprint process in the 19th century, architectural plans became more reproducible, accelerating urban development. Catalogs offering pre-designed homes became popular, democratizing homeownership.
The Digital Age and Online Architecture Design
The shift to digital drafting in the late 20th century enabled precise modeling and rapid iterations. Tools like AutoCAD, SketchUp, and BIM platforms now support detailed simulations. Online architecture design has empowered homeowners to preview floor plans, simulate materials, and collaborate with professionals remotely.
Components of an Architectural Floor Plan
Key Elements You’ll See
Architectural floor plans include:
- Walls (solid lines) indicating structural partitions
- Doors and windows (swing arcs, rectangles)
- Fixtures like sinks, bathtubs, and appliances
- Furniture placement suggestions in some residential plans
- Symbols and abbreviations, such as WIC (walk-in closet) or DW (dishwasher), crucial for interpretation
Common Scales and Measurements
Architectural plans use scale drawings to represent real dimensions. Common scales include:
- 1/4″ = 1′-0″ for floor plans
- 1/8″ = 1′-0″ for site plans
Understanding the scale notation allows homeowners to estimate room sizes, wall lengths, and furniture fit accurately.
Types of Architectural Plans
A complete set of architectural plans may contain:
- Floor Plan: A horizontal layout of spaces from a top-down view
- Site Plan: Shows the building in context with property lines, landscaping, and orientation
- Elevation Drawings: Depict the vertical exterior and interior surfaces
- Section Drawings: Cut-through views illustrating structural relationships
- Detail Drawings: Close-ups of specific features such as windows or staircases
Reading an Architectural Floor Plan Step-by-Step
Orientation and Layout
Most plans include a north arrow, helping homeowners visualize solar exposure and wind direction. Examining room flow, circulation paths, and the relationship between private (bedrooms) and public (living rooms) spaces provides insights into livability and design intent.
Structural vs. Decorative Features
It is essential to distinguish load-bearing walls from non-structural partitions. Structural elements affect what changes can be made. Decorative or interior design components, such as finishes or moldings, may not appear on basic plans but influence the final feel of the home.
Electrical and Plumbing Overlays
Plans may also include MEP overlays — Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing — showing:
- Outlets, switches, and lighting fixtures
- Plumbing lines and fixture locations
These layers are critical during kitchen or bathroom remodels, where misalignment can lead to expensive corrections.
Understanding Different Architectural Styles Through Plans
Traditional American Styles
Several traditional American architectural styles reflect distinct floor plan features:
- Colonial: Central hallway with symmetrical rooms
- Victorian: Ornate detailing and segmented rooms
- Craftsman: Built-ins, porches, and low-pitched roofs
Modern and Contemporary Layouts
Contemporary homes emphasize:
- Open floor plans that reduce partitions
- Natural light with large windows
- Indoor-outdoor integration, often with decks or patios
These plans prioritize fluidity, minimalism, and connection to nature.
Comparing Architectural Styles in Plan Form
| Feature | Colonial | Craftsman | Modern |
| Layout Symmetry | High | Moderate | Low |
| Room Division | Separate rooms | Semi-open | Open concept |
| Porch/Outdoor Access | Optional | Prominent | Integrated |
| Ornamentation | Formal detailing | Handcrafted trim | Minimalist |
Architecturally Designed Homes vs. Pre-Fab Designs
Architecturally designed homes reflect unique site conditions, client needs, and aesthetic preferences. In contrast, pre-fabricated or stock house plans are mass-produced, offering cost savings but limited customization.
Who Creates Architectural Plans? Key Figures and Roles
The Architect
Architects are certified experts trained in design, engineering principles, and building regulations. Notable figures like Frank Lloyd Wright and Julia Morgan shaped American home design with visionary plans and client-focused innovation.
Draftsperson vs. Designer
While not always licensed, draftspersons produce technical drawings based on an architect’s or designer’s vision. Designers, often specializing in interiors, may conceptualize space without producing construction-ready documents.
The Role of the Structural Engineer
For multi-level or complex homes, a structural engineer ensures stability, safety, and code compliance. They work closely with architects to verify materials, load-bearing systems, and seismic considerations.
Working with Contractors and Builders
Builders interpret architectural plans to guide construction. Clear plans reduce ambiguity and prevent on-site modifications that could compromise design or structure.
The Process Behind Architectural Plan Development
Conceptual Design Phase
Architects begin with schematic sketches and conceptual layouts to explore possibilities. These early drafts focus on spatial organization and client goals.
Design Development
The design is refined, incorporating style, structure, and systems. Materials, finishes, and architectural details begin to take shape.
Construction Documents
The finalized construction document set includes all necessary drawings for building permit approval. These plans conform to zoning regulations, safety codes, and building ordinances.
Revisions and Approval
Clients provide feedback during design development. Local authorities review final plans to ensure legal and structural compliance. Revisions may be necessary before approval.
Accessing and Using Architectural Plans Today
Where to Find Architectural Plans
Homeowners can obtain plans from:
- The original architect or builder
- Municipal building departments
- Previous owners or real estate records
- Online architecture design platforms for inspiration or pre-made layouts
Legal and Copyright Considerations
Architectural plans are intellectual property. Permission to reuse or modify them can only be granted by the copyright holder. Unauthorized reproduction or construction may lead to legal consequences.
Tips for Homeowners Reviewing Plans
Before starting a project:
- Clarify unfamiliar symbols or abbreviations
- Confirm room dimensions and traffic flow
- Verify structural elements before removing walls
- Ask for 3D models or walkthroughs when available
Architectural Plans in Media and Popular Culture
Influence of Architecture Magazines
Publications like Architectural Digest and Dwell influence design trends by showcasing innovative homes. These architecture magazines often highlight plans that reflect emerging movements such as net-zero homes or biophilic design.
Celebrity Homes and the Growing Popularity of the Plan Aesthetic
Social media platforms and real estate showcases have popularized the aesthetic appeal of architectural plans. Floor layouts of celebrity homes are widely shared, encouraging broader architectural literacy and appreciation.
Conclusion: Why Architectural Literacy Matters
Architectural plans are more than technical drawings—they represent the foundation of our built environment. For homeowners, understanding these documents fosters better communication, smarter investment, and deeper appreciation of design. With access to online architecture design tools, educational resources, and expert guidance, architectural literacy is more attainable than ever. Lifelong learning through books, design courses, or even a subscription to an architecture magazine can enrich both your home and mind.
Frequently Asked Questions (SEO FAQ Block)
What is included in an architectural floor plan?
A typical floor plan includes walls, doors, windows, fixtures, and sometimes furniture. It shows spatial relationships and is drawn to scale.
How do I read my house’s architectural plans?
Start by identifying the scale and orientation, then examine room labels, symbols, and structural features like load-bearing walls.
Can I design my own house plan online?
Yes. Several online architecture design platforms allow homeowners to create and modify house plans, though professional review is recommended.
How do architectural drawings differ from structural drawings?
Architectural drawings emphasize design, layout, and visual elements, whereas structural drawings outline the framework, load-bearing components, and material specifications.
Are architectural plans required for remodeling?
For significant remodels, yes. Most municipalities require updated plans to issue permits and ensure code compliance.
What is the cost of getting an architectural plan done?
Costs vary by project scope and region. Custom home plans from licensed architects can range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars.